How UPI payment gateway works?
So, What exactly is UPI?

Unified Payments Interface is an instant real-time payment system developed by National Payments Corporation of India facilitating inter-bank transactions. The interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and works by instantly transferring funds between two bank accounts on a mobile platform.
Some simple examples ybl and axis are two banks that provide virtual payment addresses. And, alice and bob are the unique identifiers in respective address providers.Just like how domains get resolved to IP addresses, every VPA needs to be linked to a bank account. In short, a UPI Virtual Payment Address serves as the addressing layer for a bank account.
There are mainly two types of transactions in the UPI realm.
Direct Payment:
The payer (the sender) initiates the transaction. Typical examples would be, you paying a shopkeeper at the checkout by scanning a QR code or you sending money to your friends and family.
Collect Request:
The payee (the receiver) initiates the transaction. A simple example is a scenario where your landlord creates a collect request asking you to pay the monthly rent.
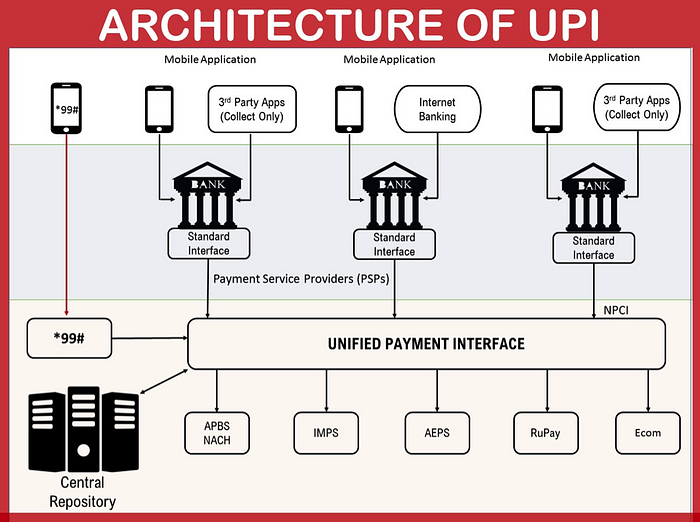
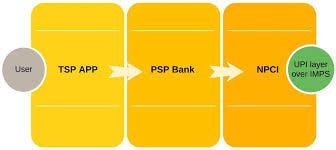
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN TRANSFER THE MONEY BY UPI?
There are three types of participants in the UPI ecosystem.
The Banks
- Banks hold your money. UPI works directly with the bank accounts. The bank account will be debited from or credited to whenever you send money or receive money.
- The banks that hold your money are also called Issuing Banks.
- Every bank uses a system called Core Banking System (CBS) to manage its user’s accounts. At the core, CBS is a simple CRUD system built around user accounts.
- Debit and Credit are the two fundamental operations of core banking software.
The Payment Apps

- Payment Apps are consumer-centric products that can be used to link a bank account and transact in the real world. Some major apps are Google Pay, PhonePe, BHIM, etc. Almost all the banks have their own versions of UPI Apps. There is a wide variety of options to chose from.
- Payment Apps allow users to create handles to make everyday transactions easier. However, not everyone can start creating UPI handles. Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates who can create UPI handles.
- That’s why all the payment apps will have to tie up with banks. These banks not only allow payment apps to create and manage UPI handles for their users, but they are also the interface to the UPI ecosystem.These banks are called Acquiring Banks.
NPCI

- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) is a non-profit set up by the Government of India to facilitate digital payments. They facilitate many payment schemes (like IMPS, BBPS, FASTag, etc.)
- This approach is the same as building an Internet where your browser has to remember the IP address of every possible website on the planet, otherwise, you wouldn’t be able to access it.
- The job of resolving every web address into an IP address is taken out as a separate protocol called DNS. Our browsers trust the IP address resolved by the DNS servers used by our Internet Service Providers.
- That’s the route UPI creators took, they made NPCI as the trusted switch and they standardized the protocol. NPCI makes sure that data flow between banks and payment apps are routed to the correct and verified destinations.
- Apart from being the trusted router, NPCI also hosts non-financial meta APIs to serve everyone in the ecosystem. NPCI has one more important role to play. It’s something to do with settlement.
